A Guide to Open Banking: Changes, Challenges and the Road Ahead
Deloitte defines open banking as a ubiquitous financial trend that is here to stay and is going to have a lot of say in the evolving financial world and traditional banking systems. Being a platform-based business approach, open banking is an ecosystem of banks, customers, third-party developers, partners and FinTech companies.
So, the data, processes and business functionalities are made available to each of these stakeholders and might come from any one of them.

As per the recent stats, open banking is a business opportunity with more than $8 billion US dollar revenue and, one of the most challenging disruptions for the traditional banking system and financial sector.
Take a look at the following graph that shows the projections of open banking users across the world from 2020 to 2024:
It clearly shows the number is going towards a steep incline in the major continents, such as Europe, China and far Eastern Countries and the entire world, in general.
But, then again, what is the entire concept of open banking, and why is it becoming so popular? Are there any benefits from the emerging trends, and is the concept going to pose any challenges for the well-established banking system? Finally, what are its short-term far-reaching impacts on the FinTech sector, banking technologies and the entire financial ecosystem of the world?
We explore the answers to all these and many other questions in the following sections and discover how Africa is emerging as a dynamic entity on the transitive landscape of open banking.
Let us begin with a general introduction of the term and the entire concept.
Open Banking - The Concept and Details
Open banking is a system that connects banks, technical providers and third parties, and enables them to exchange data to their customers’ benefit in a secure and simple manner. It allows this by enabling an entire world of innovative apps and services that are tailored to customers’ financial data.
So, they can move, manage and make more of their money and leverage these apps and services for better and more defined control over their finances.
The customers can keep a track of their money and make online transactions via their banks on a real-time basis. As the third parties have access to the banking data and financial information of the customers, they can create more suitable and tailor-made digital tools and apps to elevate the levels of customer satisfaction and experiences.
The third parties can design and deliver financial tools that allow the people more control over their money, and expenses. These tools raise the potential of revenue and satisfaction for both the banks and the customers, and allow more thorough data sharing across all the partners of the open banking system in an easy and secure manner.
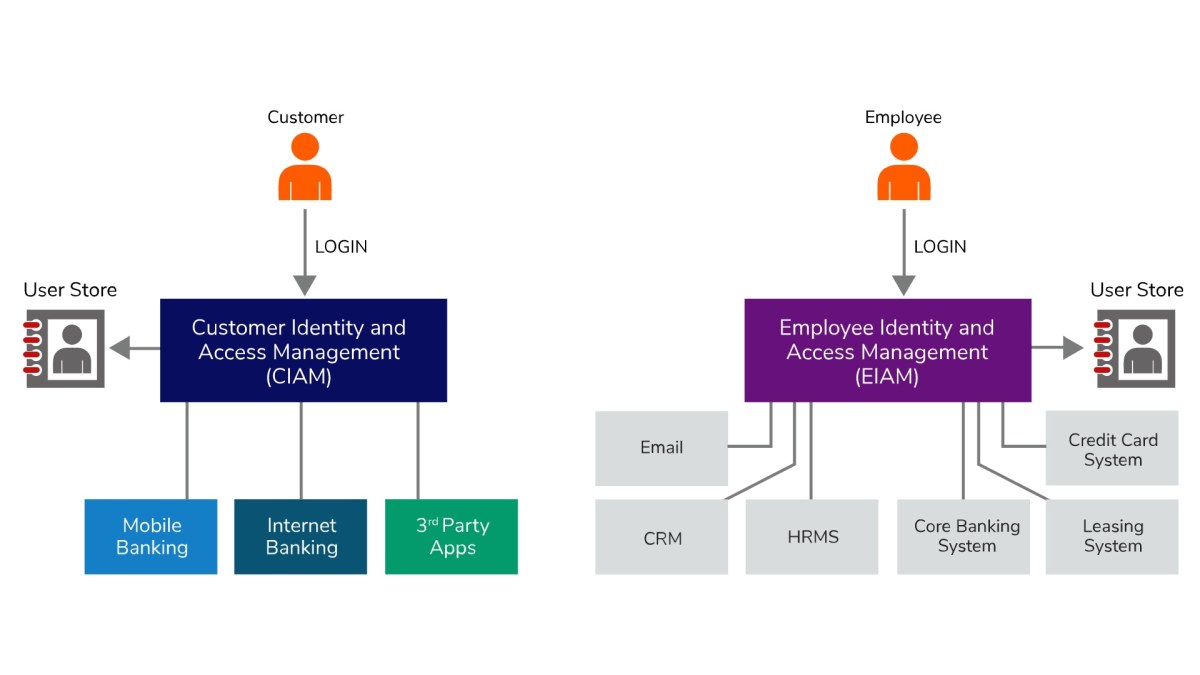
Take a look at the following screenshot to find more about the open banking system, or to understand what happens in an open banking system:
The customers can log into the open banking system and access all the standard banking facilities, such as mobile banking and internet banking, as well as the third-party apps from the user store.
Likewise, the employees of the open banking system also have to access the system securely to manage the various controls, such as HRMS, CRM, Email system, Core Banking System, Credit Card System and Leasing System etc. They also have a user store for third-party apps and technological tools that varies across the different open banking systems and allows them to deliver more delightful and more meaningful customer experiences.
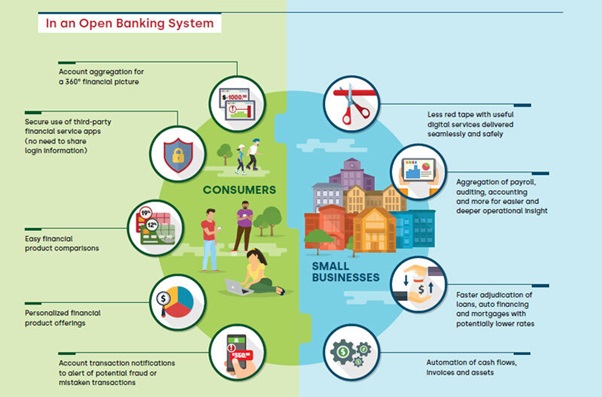
Let us take a look at another picture that showcases the various how-to’s of an open banking system via use case instances:
By now, you might have amassed a thorough understanding of the open banking system.
Next, we discuss the various countries and regions with the highest number of open banking users.
Open Banking Users - Regions, Countries, and Trends
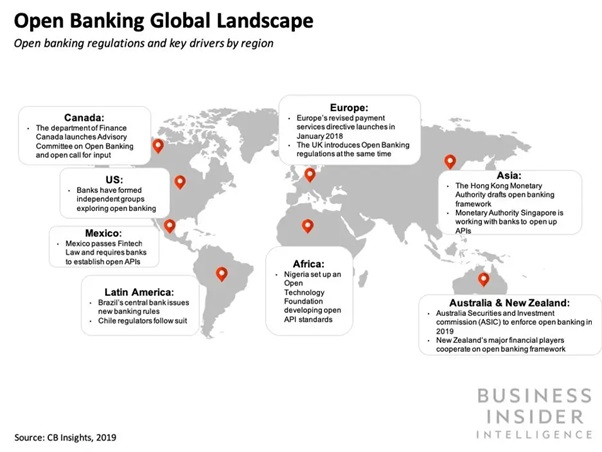
Before we dive into the deeper waters, let us take a look at the following screenshot from a recent Business Insider feature that shows the recent efforts in the direction of open banking across the world:
Hence, the major zones of open banking systems are – UK, Europe, Australia, Hong Kong and Africa. While the UK is certainly the “cradle of open banking“, the EU is also emerging as a top player in the sector.
There were 204 regulated open banking providers in the UK as of January 2020, and the country is often touted as a trailblazer in the sector.
In the EU, Germany, Luxembourg and Italy are the countries where open banking is used predominantly. However, the pan-European payments system “The Berlin Group” has more than 40 open banks that are used across Europe.
Emerging Players
- The countries like India, Singapore, Japan and South Korea don’t have any formal or compulsory open banking regime as of now. However, the policymakers are taking a range of measures for promoting and accelerating the take-up of data sharing platforms in banking.
- The US is also opting for a market-led approach, but as of now, there is no support or initiatives from the government. On the other hand, Mexico and Latin America have already started working towards the system.
- Outside EU, Singapore, Hong Kong and Australia are the two major jurisdictions that have opted for a regulatory-driven approach towards open banking.
- China is yet another country where open banking is considered an integral part of FinTech yet, the country is in the infant stages of establishing universal industry standards.
- In Africa, Rwanda, Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa are the major hubs of open banking and Mozambique, Tanzania, Zambia, and Uganda are emerging as major open banking areas. Apart from spurring financial independence, open banking will also bring about financial inclusion of the unbanked and under-banked populations.
Predicting the Trends
Open banking initiatives are still in the very early stages of establishment and implementation and more contribution is required from the firms, regulators, policymakers and government.
While the system establishment itself is not that daunting a task, ensuring the safety, ease of use and security in the entire ecosystem is still going to take a long time for proper establishment.
However, there is no doubt that open banking and cross-industry data sharing ecosystem are the way forward for the future banking and financial ecosystem.
Open Banking System - Introduction and Implementation in a Market
For the implementation, the traditional banking and financial institutions open up their application programming interfaces or APIs to third parties. The third-party apps will have their own set of functionalities and services and access the customer data securely.
Open banking is entirely secure, and every transaction and process requires approval and authentication from the customer. So, no information or data is shared or used without the consent of the customer.
Once the customer has given consent, the third-party financial service providers will access the banking data via their APIs and create better services and apps for financial management and general monetary use.
Hence, there is an integration of services between the bank and third parties to leverage the existing banking data of the customer for delivering customer prompts and services that ensure better and smarter use of their money.
What do Data Sharing and Open Banking mean to the Customer?
Customer banking data is the collection of all the banking activities, such as:
- How is the customer spending money?
- How is he saving the money?
- Is the debt growing?
- How to ensure better savings, spending and investment habits? etc
Hence, this data offers the exact persona of a customer as an entity in the economy. Currently, this information is collected and sent manually to compile the financial information across all the money-related platforms.
When you use open banking, the data compilation will be done in a universally recognized format and can be accessed by various stakeholders of your open banking system. This will allow the financial institutions to offer a number of innovative products and services for financial management.
Some of the benefits these products and services will offer are:
- In-depth analysis of earnings, spending, and savings for better budgeting
- Better product recommendations in relation to better interest rates, returns and capital investment etc
- Better repayment plans
- Loans with tailored services and convenient structures
- Improved processing and information sharing while applying for loans etc.
Hence, the open banking services will be more tailored and highly specific or personalized for every customer. This will improve the customer experiences and make the banking sector extremely customer-oriented.
Open Banking - Challenges and Threats
When we talk about having a universal banking and a financial system where the banks are interacting with the third-party apps and interfaces, security concerns, proper integration platforms, and technological concerns take a crucial stance.
There is a certain and evident gap between the current FinTech technology and the highly comprehensive open banking system that is secure, legal and standardized at a large scale. Hence, there is a dire need of bridging this gap with proper APIs and technologies in finances, banking, digital and security sectors.
The open banking platforms have already emerged as major industry disruptors across a number of countries where the traditional banking system is extremely well-established. Asia Pacific countries, the US and UK are some of the best examples in this regard.
So, there are not only impending challenges but “threats” to these established banking systems and the FinTech sector, in the light of Open Banking!
Let us take a look at the various changes open banking spurred in the financial ecosystem of Africa.
Open Banking in Africa - Changes and Threats
1. FinTech: Smartphones and internet access generated a breed of technology savvy and information-equipped young Africans that started solving problems for themselves and their communities. They figured out the new channels for financial inclusion and proper banking, such as mobile money, cross border financing and open banking.
Hence, the FinTech sector is spangled with disruptions and as of now, a number of mobile-based app businesses are thriving in the financial sector.
2. Technology: Numerous brick and mortar businesses have failed to embrace this new wave of digital transformation because of the lack of proper technology and the availability of only a handful of legal and comprehensive open banking entities.
3. Data: FinTech companies and data scientists are mobilising and processing the huge chunks of banking data that was sitting idle in the files and storage database of banks. This data is then used to create and deliver highly customized and personalized services and products for every customer.
Now, the banks are getting the nudge to embrace third-party apps to ensure that they remain in the business, spurring the financial inclusion of the underbanked or unbanked African population.
4. Skillset: FinTech companies are looking for talents with skills for developing APIs and tools or products for better and easier financial management.
Areas where open banking is being witnessed as a threat:
- Cybersecurity
- Technology
- Traditional banking
- Regulation of financial processes
- Internet-based financial activities
So Who Comes Out Winning?
At the end, what open banking provides is the overall regulatory framework and the ecosystem which will permit all the financial players in a market to have a fair shot at exceling their service provision to end users. So who would fail and who would win? Well, putting it in a very simple statement, those who can provide financial services consumers actually need at a competitive price, with a simple user experience, in a fast & secure manner, would come up winning. Sounds quite easy and logical, doesn’t it? Well, not quite! The two main fundamental components here would be the technology platform adopted that would be the critical means to deliver and make all the above actually happen, in addition to the establishment of a very lean operational backend to enable cost effective and fast delivery services to the consumers yet complying with security and risk regulations. The security & and risk components could be pretty straightforward that would be mainly dictated by a set of minimal standards set out by regulators within each financial market or within larger regional trade pacts such as within the EU. However, where most still struggle is what is the technology impact on all this and how choosing the right one and a cost effective one would dramatically affect the service provider’s capability to deliver in the manner stated above. How agile the technology platform is in customizing certain financial services and delivering it real time across all digital channels making easily accessible to consumers with flexibility in adjusting business and risk parameters based on the product, the capability of building different digital frameworks on a microservice level that would easily allow for service providers to expand their vertical business offerings from lending to saving to different investment products using that same platform, is a whole different ball game all together and inevitably a game changer!
CIT Vericash, has taken an interesting approach towards this, with its generic digital financial service delivery platform. Being a predominantly African company, it has grasped the opportunity of the initial stages of adoption amongst several of the key African markets for placing the first founding bricks of an open banking ecosystem, and has taken a closer look into how to further adapt its already agile platform into enabling many of the new Fintech startups, or incumbent banks, for that matter, to adopt its platform to be able to deliver their financial services in a real-time manner providing a quick time to market launch with the flexibility and ease to customize and adapt according to market changes and demands, all this at a cost effective business model that allows for a maximum cost streaming by many of these service providers. It has already initiated several projects with some of the regulators and certain key markets to put the effectiveness to test.
It is up to the banks to be able to provide a nimble UX providing their customers with a unique and friendly customer experience. More importantly, it is of paramount importance that they control and own the entire visibility of all financial and non-financial data of their customers which is really the main value of this whole process from which endless added value services could be provided and personalized to each customer segment. Vericash’s agile digital platform enables these flexible customizations for each side of the spectrum, whether you are a large bank, a small one or a Fintech entering to compete.
Open Banking - Key Takeaways
While the open banking system is one of the most promising banking industry disruptions, it brings a lot of challenges and bottlenecks with it. The technology sector itself needs to be more agile, secure, flexible and accommodating for the development of better and smarter APIs for inter-platform transactions. Data processing and analytics need to be more prepared for dealing with huge chunks of data that are lying useless and untouched for decades in the banks.
Also, the data collection also needs to be more versatile for including the underbanked and unbanked population clusters.
Finally, the security and comprehensive operations are still going to take many years to be completely ready for a large-scale implementation and standardization of open banking systems.
About CIT Vericash
CIT VERICASH is a division of CIT GLOBAL, an international leading provider of innovative eCommerce and mCommerce software solutions and services with solid expertise spanning 25 years, since its establishment in Toronto, Canada in 1993. By applying CIT Global’s dedicated centers of excellence and its specialized leading products, in cooperation with its strategic partners, the company has delivered innovative and award-winning solutions to its clients in more than 48 countries, serving leading brands from North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa.